Info
This feature is only available in the unlimited plan.
Example 1: Code for the automatic creation of footnotes
1. How the macro works:
Example:
Lorum voluptua.{FN:ICC-01/09-02/11; emphasis} At vero eos et accusam et justo duo dolores et ea rebum. Stet clita kasd gubergren, no sea takimata sanctus est Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet.{FN:ICC-01/09-02/11; emphasis}
Ω
Tipp
There should not be a space between the footnote and the referenced word or sentence, otherwise this space will remain with the later footnote number and the referenced sentence or word.
2. Format templates used
The standard Word styles are used. For deviating changes in the presentation of the footnote itself, this is the format template "Footnote text". For an individual adaptation of the footnote number, the format template "Footnote characters" in the letterhead must be adapted.
3. Code example
There are many different ways of programming such a macro. Please feel free to contact our support. Here is an example of a macro:
Sub AutoOpen()
Dim OpenStrg As String
Dim CloseStrg As String
Dim myRange As Range
Dim StartPos As Long
Dim EndPos As Long
OpenStrg = "{FN:"
CloseStrg = "}"
StartPos = InStr(1, ActiveDocument.Range.Text, OpenStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Do Until StartPos = -1
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Range
EndPos = InStr(StartPos, ActiveDocument.Range.Text, CloseStrg, vbTextCompare)
myRange.SetRange Start:=StartPos, End:=EndPos
ActiveDocument.Footnotes.Add Range:=myRange, Text:=Mid(myRange.Text, Len(OpenStrg) + 1 Len(myRange.Text) - Len(CloseStrg) - Len(OpenStrg))
myRange.Text = ""
StartPos = InStr(StartPos, ActiveDocument.Range.Text, OpenStrg,vbTextCompare) - 1
Loop
End SubNote: There are restrictions in the functioning of the macro if the document contains function fields (e.g. tables of contents) or clickable URLs ("::url"). An alternative to this is shown below.
4. Code example for documents with function fields and/or clickable URLs
Sub AutoOpen()
Dim OpenStrg As String
Dim CloseStrg As String
Dim myRange As Range
Dim myPara As Paragraph
Dim StartPos As Long
Dim EndPos As Long
OpenStrg = "{FN:"
CloseStrg = "}"
For Each myPara In ActiveDocument.Paragraphs
StartPos = InStr(1, myPara.Range.Text, OpenStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Do Until StartPos = -1
Set myRange = myPara.Range
EndPos = InStr(StartPos, myPara.Range, CloseStrg, vbTextCompare)
myRange.SetRange Start:=myRange.Start + StartPos, End:=myRange.Start + EndPos
ActiveDocument.Footnotes.Add Range:=myRange, Text:=Mid(myRange.Text, Len(OpenStrg) + 1, Len(myRange.Text) - Len(CloseStrg) - Len(OpenStrg))
myRange.Text = ""
StartPos = InStr(StartPos, myPara.Range, OpenStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Loop
Next
End SubNote: Since the macro searches each paragraph individually and finds and creates footnotes, it is important that there are always only footnotes OR function fields or hyperlinks ("::url") in a paragraph. If this is not the case, display problems may occur. In addition, care must be taken that the marking of a footnote "{FN:...} is always within a paragraph and not across several paragraphs.
5. Code to prepare footnotes for the import
If you want to import a text that already contains footnotes and want to display them as such again in the export, you can also use a macro for this. The following macro converts your footnotes into the format described above ("{FN:...}"). This way you can prepare extensive texts with footnotes appropriately.
Sub Re_FN_UPdated_3()
Dim FtNt As Footnote
Dim FNTxt
For Each FtNt In ActiveDocument.Footnotes
With FtNt.Reference
.Font.Superscript = False
FNTxt = FtNt.Range.Text
If Asc(Left(FNTxt, 1)) = "2" Or Asc(Left(FNTxt, 1)) = "9" Then
FNTxt = Right(FNTxt, Len(FNTxt) - 1)
If Asc(Left(FNTxt, 1)) = "9" Then
FNTxt = Right(FNTxt, Len(FNTxt) - 1)
.Text = "{FN:" & FNTxt & "}"
Else
.Text = "{FN:" & FNTxt & "}"
End If
Else
.Text = "{FN:" & FtNt.Range.Text & "}"
End If
End With
Next
End SubTo convert the expressions back to footnotes in the export, you can use the first macro again!
Example 2: Code for the automatic creation of checkboxes, text fields and write protection.
1. How the macro works:
{□} Option 2
Name: {…}
Adress: {…}
Important:
When you insert “…” in Word it typically converts it to a single object. So be sure to press the backspace key in order to prevent this automated formatting.
2. Code example
Sub CreateContentControls()
Dim CheckboxStrg As String
Dim TextboxStrg As String
Dim myRange As Range
Dim Testrange As Range
Dim StartPos As Long
Dim EndPos As Long
Dim Password As String
Dim Deletepath As String
Password = "1234"
CheckboxStrg = "{" & ChrW(&H25A1) & "}"
TextboxStrg = "{...}"
Offset = 0
StartPos = InStr(1, ActiveDocument.Range.Text, CheckboxStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Do Until StartPos = -1
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Range
Set Testrange = ActiveDocument.Range
Testrange.SetRange Start:=1, End:=StartPos
Offset = Testrange.ContentControls.Count * 2
EndPos = StartPos + Len(CheckboxStrg)
myRange.SetRange Start:=StartPos + Offset, End:=EndPos + Offset
myRange.Select
myRange.Text = ""
myRange.ContentControls.Add (wdContentControlCheckBox)
StartPos = InStr(StartPos, ActiveDocument.Range.Text, CheckboxStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Loop
StartPos = InStr(1, ActiveDocument.Range.Text, TextboxStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Do Until StartPos = -1
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Range
Set Testrange = ActiveDocument.Range
Testrange.SetRange Start:=1, End:=StartPos
Offset = Testrange.ContentControls.Count * 2
EndPos = StartPos + Len(TextboxStrg)
myRange.SetRange Start:=StartPos + Offset, End:=EndPos + Offset
myRange.Select
myRange.Text = ""
myRange.ContentControls.Add (wdContentControlText)
StartPos = InStr(StartPos, ActiveDocument.Range.Text, TextboxStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Loop
Application.ActiveDocument.Protect wdAllowOnlyFormFields, Password:=Password
Deletepath = ActiveDocument.FullName
ActiveDocument.SaveAs2 FileName:=Left(ActiveDocument.FullName, Len(ActiveDocument.FullName) - 5) & ".docx", FileFormat:=wdFormatDocumentDefault
Documents.Open (Left(ActiveDocument.FullName, Len(ActiveDocument.FullName) - 5) & ".docx") Kill (Deletepath)
End SubNote: There are restrictions in the functioning of the macro if the document contains function fields (e.g. tables of contents) or clickable URLs ("::url"). In addition, difficulties may arise if the above-mentioned expressions "{□}" or "{...}" are used in tables. An alternative to this is shown below.
Example 3: Code for documents with function fields, tables or clickable URLs.
If your document is to contain other function fields in addition to footnotes, such as tables of contents or clickable links ("::url"), or if the expressions "{□}" or "{...}" are to be placed in tables, it is necessary to use an appropriately adapted macro. In the following we provide you with a sample code:
Sub CreateContentControls()
Dim CheckboxStrg As String
Dim TextboxStrg As String
Dim myRange As Range
Dim Testrange As Range
Dim myPara As Paragraph
Dim StartPos As Long
Dim EndPos As Long
Dim Password As String
Dim Deletepath As String
Password = "1234"
CheckboxStrg = "{" & ChrW(&H25A1) & "}"
TextboxStrg = "{...}"
Offset = 0
For Each myPara In ActiveDocument.Paragraphs
StartPos = InStr(1, myPara.Range.Text, CheckboxStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Do Until StartPos = -1
Set myRange = myPara.Range
Set Testrange = myPara.Range
Testrange.SetRange Start:=myRange.Start, End:=myRange.Start + StartPos + 1
Offset = Testrange.ContentControls.Count * 2
EndPos = StartPos + Len(CheckboxStrg)
myRange.SetRange Start:=myRange.Start + StartPos + Offset, End:=myRange.Start + EndPos + Offset
myRange.Select
myRange.Text = ""
myRange.ContentControls.Add (wdContentControlCheckBox)
StartPos = InStr(StartPos + 1, myPara.Range.Text, CheckboxStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Loop
Next
For Each myPara In ActiveDocument.Paragraphs
StartPos = InStr(1, myPara.Range.Text, TextboxStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Do Until StartPos = -1
Set myRange = myPara.Range
Set Testrange = myPara.Range
Testrange.SetRange Start:=myRange.Start, End:=myRange.Start + StartPos + 1
Offset = Testrange.ContentControls.Count * 2
EndPos = StartPos + Len(TextboxStrg)
myRange.SetRange Start:=myRange.Start + StartPos + Offset, End:=myRange.Start + EndPos + Offset
myRange.Select
myRange.Text = ""
myRange.ContentControls.Add (wdContentControlText)
StartPos = InStr(StartPos + 1, myPara.Range.Text, TextboxStrg, vbTextCompare) - 1
Loop
Next
Application.ActiveDocument.Protect wdAllowOnlyFormFields, Password:=Password
Deletepath = ActiveDocument.FullName
ActiveDocument.SaveAs2 FileName:=Left(ActiveDocument.Name, Len(ActiveDocument.Name) - 5) & ".docx", FileFormat:=wdFormatDocumentDefault
Documents.Open (Left(ActiveDocument.Name, Len(ActiveDocument.Name) - 5) & ".docx")
Kill (Deletepath)
End SubATTENTION: Since the macro searches each paragraph individually for the expressions, it is important that there are only expressions OR function fields or hyperlinks ("::url") in a paragraph. If this is not the case, display problems may occur. In addition, care must be taken that the marking of the check boxes and text fields with the expressions "{□}" or "{...}" always occurs within a paragraph and not across several paragraphs.
Example 4: Code for automatic formatting of footnotes
1. How the macro works:
The aim is to automatically implement the formatting shown below:

2. Code example
There are many different ways of programming such a macro. Please feel free to contact our support. Here is an example of a macro:
Sub FormateFootnotes()
For i = 1 To ActiveDocument.Footnotes.Count
ActiveDocument.Footnotes(i).Range.Select
With Selection
.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseStart
.MoveLeft Unit:=wdCharacter, Count:=1, Extend:=wdExtend
.TypeText Text:=vbTab
.ParagraphFormat.FirstLineIndent = CentimetersToPoints(-1.5)
End With
Next
Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogSaveAs).Show
End Sub
Example 5: Code for inserting tab stops within a paragraph
1. How the macro works:
The alignment of text in Lawlift is usually done via the formatting of the individual paragraphs. In order to indent text areas within a paragraph, the following macro is available.
How to insert the code and set the tab stops is explained in detail here.
2. Code example:
There are many different ways of programming such a macro. Please feel free to contact our support. Here is an example of a macro:
Sub AutoOpen()
'
' Tabstopp Makro
'
'
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Content
myRange.Find.Execute FindText:="{Tab}"
With Selection.Find
.ClearFormatting
.Text = "{Tab}"
.Replacement.ClearFormatting
.Replacement.Text = "^t"
.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll, Forward:=True, _
Wrap:=wdFindContinue
End With
End SubExample 6: Code for marking unfilled placeholders
1. How the macro works:
This macro offers you the function to highlight unfilled placeholders in your Word document in color. After inserting the code the placeholders that have not been filled in are automatically highlighted in yellow when the Word document is opened.
2. Code example:
There are many different ways of programming such a macro. Please feel free to contact our support. Here is an example of a macro:
Sub AutoOpen()
'
' Makro1 Makro
'
'
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Content
myRange.Find.Execute FindText:="[...]"
Options.DefaultHighlightColorIndex = wdYellow
myRange.Find.ClearFormatting
myRange.Find.Replacement.ClearFormatting
With myRange.Find
.Replacement.Highlight = True
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindAsk
.Format = True
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchWildcards = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
End With
myRange.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End Sub
Example 7: Prepare formatted links for Lawlift import
1. How the macro works:
Lawlift offers you the possibility to format a URL inserted as a hyperlink with a title using the "title(...)" function. We have shown you here exactly how this works.
However, if you have a Word document in advance that is to be automated and already contains such formatted links, you cannot simply copy the text into LAWLIFT. Only the titles would be copied, but not the URLs.
A macro can help here, which converts all formatted links in the Word document into the form "::url[www.exampleurl.de title(example)]" readable by LAWLIFT. Afterward, the formatted links can simply be copied from the Word file into the LAWLIFT template. Lawlift recognizes the expressions and inserts them as clickable URLs with the given title, as shown in our help.
Unformatted links can also be simply copied into the LAWLIFT template without using this macro and LAWLIFT recognises them as such.
2. Code example:
There are many different ways to program a macro. Please feel free to contact our support.
Here is an example of a macro that prepares the source file for import into Lawlift:
Sub Format_Hyperlinks()
Dim Link As Hyperlink
Dim HTP1, HTP2 As Integer
HTP1 = 0
HTP2 = 0
'checking document if it contain URLs
If ActiveDocument.Hyperlinks.Count > 0 Then
For Each Link In ActiveDocument.Hyperlinks '------------------------
If Link.Address <> "" Then
'links vs bookmarks
If InStr(Link.Address, "http") > 0 Then '------------
Link.Range.Select
'checking for address only links
If Link.TextToDisplay = Link.Address Then
Selection.TypeText "::url[" & Link.Address & "]"
HTP1 = HTP1 + 1
Else 'if link have a text to display
Selection.TypeText "::url[" & Link.Address & " Title(" & Link.TextToDisplay & ")]"
HTP2 = HTP2 + 1
End If
End If '------------
End If
Next Link '------------------------
'statistic message
mSg = "There are " & HTP1 & " link(s) without Title." & Chr(13) & "There are " & HTP2 & " link(s) with Title." & Chr(13) & "Total " & HTP1 + HTP2 & " link(s) formatted so far."
MsgBox mSg, vbOKOnly + vbInformation, "Statistics"
Else
'if not links were found in document
MsgBox "There are no hyperlinks in this document."
End If
End Sub
Sub Format_Hyperlinks_Updated()
'------------------------------------------------'
'--------- Dealing Hyperlinks in Body -----------'
'------------------------------------------------'
Dim Link As Hyperlink
Dim HTP1, HTP2 As Integer
HTP1 = 0
HTP2 = 0
BD = 0
FT = 0
'checking document if it contain URLs
On Error Resume Next ' Handling unknown error for this time only
If ActiveDocument.Hyperlinks.Count > 0 Then
For Each Link In ActiveDocument.Hyperlinks '------------------------
'links vs bookmarks
If InStr(Link.Address, "http") > 0 Then '------------
Link.Range.Select
'checking for address only links
If Link.TextToDisplay = Link.Address Then
Selection.TypeText "::url[" & Link.Address & "]"
HTP1 = HTP1 + 1
Else 'if link have a text to display
Selection.TypeText "::url[" & Link.Address & " Title(" & Link.TextToDisplay & ")]"
HTP2 = HTP2 + 1
End If
End If
BD = BD + 1
Next Link '------------------------
Else
'if not links were found in document
MsgBox "There are no hyperlinks in the body of document."
End If
'------------------------------------------------'
'------- Dealing Hyperlinks in Footnotes --------'
'------------------------------------------------'
Dim h As Hyperlink
With ActiveDocument
If .Footnotes.Count >= 1 Then
With .StoryRanges(wdFootnotesStory)
For Each h In .Hyperlinks
If InStr(h.Address, "http") > 0 Then
h.Range.Select
'checking for address only links
If h.TextToDisplay = h.Address Then
Selection.TypeText "::url[" & h.Address & "]"
HTP1 = HTP1 + 1
Else 'if link have a text to display
Selection.TypeText "::url[" & h.Address & " Title(" & h.TextToDisplay & ")]"
HTP2 = HTP2 + 1
End If
End If
FT = FT + 1
Next h
End With
End If
End With
'------ Statistic Message -------'
mSg = "Number of Hyperlink(s) in:" & Chr(13) & "Main Document =" & BD & Chr(13) & "Footnote =" & FT & Chr(13) & Chr(13) & "There are " & HTP1 & " link(s) without Title." & Chr(13) & "There are " & HTP2 & " link(s) with Title." & Chr(13) & Chr(13) & "Total " & HTP1 + HTP2 & " link(s) formatted so far."
MsgBox mSg, vbOKOnly + vbInformation, "Statistics"
End SubNote: Only run the macro once, otherwise the functions will nest inside each other.
Example 8: Code for setting a numbering within tables
1. How the macro works:
The numbering of rows in a table basically works like the usual numbering in Lawlift, namely via levels. In order to identify these levels within the table, the expression "[#]" is used. Here "[#]" defines the 1st level, "[##]" the 2nd level, "[###]" the 3rd level and so on. All nine levels provided by Word can be used. Which numbering is finally inserted must be determined beforehand in a list format template within the letterhead. The name of the list format template is of particular importance, as the name is used in the macro. In our case, the list was named "A. / 1 . / 1.1.". However, you can also give the list a different name and adapt the macro code accordingly.
If you have any questions about this, please contact our support team at support@lawlift.de.
2. Code example:
Below you will find a sample code that applies the numbering defined in the list format template to the paragraphs within a table. These paragraphs must first be marked with [#], [##], etc. in the LAWLIFT template. As soon as the macro is executed, the numbering is added in the corresponding places. Please note that the numbering outside the table is also taken into account here.
Strictly speaking, the code example consists of two different sub-routines. The first determines that all numbering levels are aligned to the left. This ensures a clear presentation within the table, where there is often not much space for indentations. The second sub-routine then converts all paragraphs marked with the [#] commands into numbered paragraphs and is based on the numbering previously defined in the list format template "A. / 1 . / 1.1.".
If there are a large number of expressions in the document, the execution may take a few seconds.
Sub Level_setting_A_1_11()
Dim X As Integer
Const newNumPos As Long = 0
Const newTextPos As Long = 0
With ActiveDocument.Styles("Liste3").ListTemplate
For X = 1 To 9
.ListLevels(X).TextPosition = newTextPos
.ListLevels(X).NumberPosition = newNumPos
Next
End With
End Sub
Sub Nummerierung_Numeric_with_Zero_indentation()
Dim Level As Integer
With ActiveDocument.Range.Find
.Text = "\[#*\]"
.MatchWildcards = True
Do While .Execute
If .Parent.Information(wdWithInTable) Then
Level = Len(.Parent.Text) - 2
.Parent.Style = ActiveDocument.Styles("Liste3")
.Parent.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = Level
If Not Level = 1 Then
.Parent.ListFormat.ListTemplate.ListLevels(Level).TextPosition = 0
.Parent.ListFormat.ListTemplate.ListLevels(Level).NumberPosition = 0
End If
.Parent.Delete
End If
Loop
.MatchWildcards = False
End With
End Sub
Example 9: Code for generating variable numbering of attachments
1. How the macro works:
This code example offers you the possibility to number attachments variably and to set interactive references in the text. To do this, use the expression "{#VN}", which is placed in the place of the respective numbering, followed by the individual name of the attachment. For the references in the text, the expression "(...Attachment {#VN}: Name_of_the_attachment)" is used.
2. Code example:
There are some special features to be observed when using the macro. To ensure proper functioning, the template must contain the heading "Attachments". In addition, the attachments must be displayed in a numbered list. In the following, you will find an illustration of how the macro works:
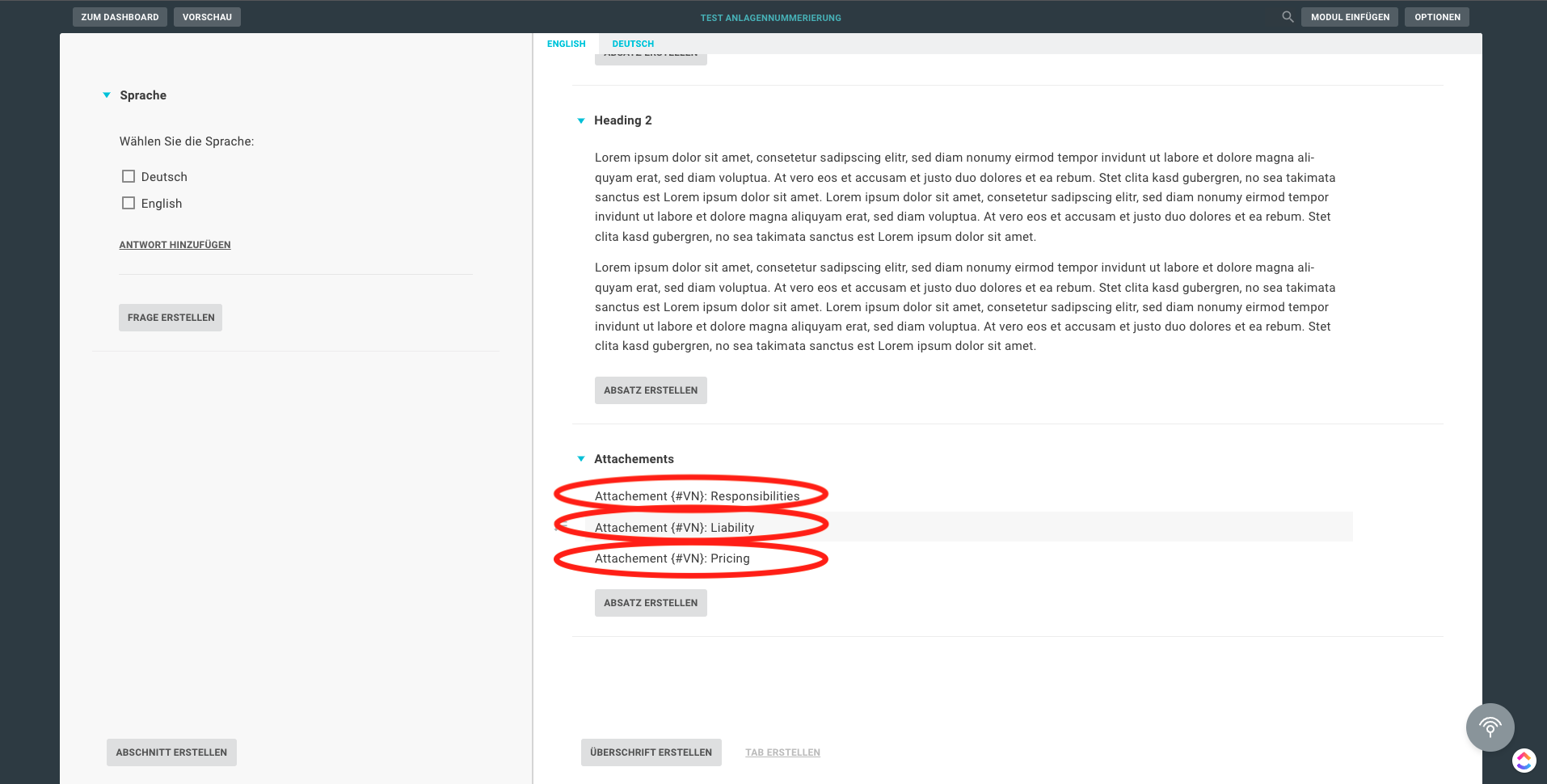
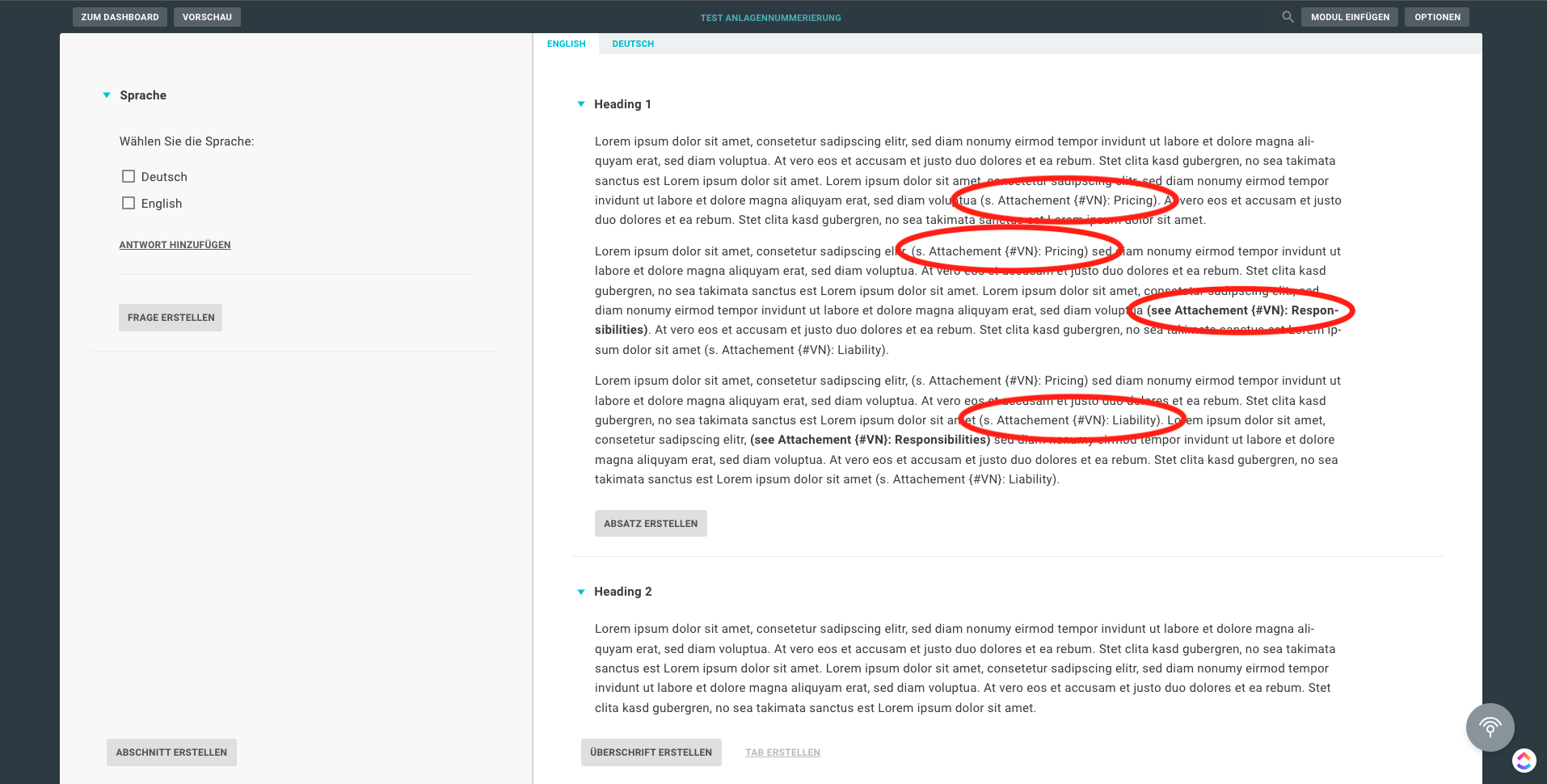
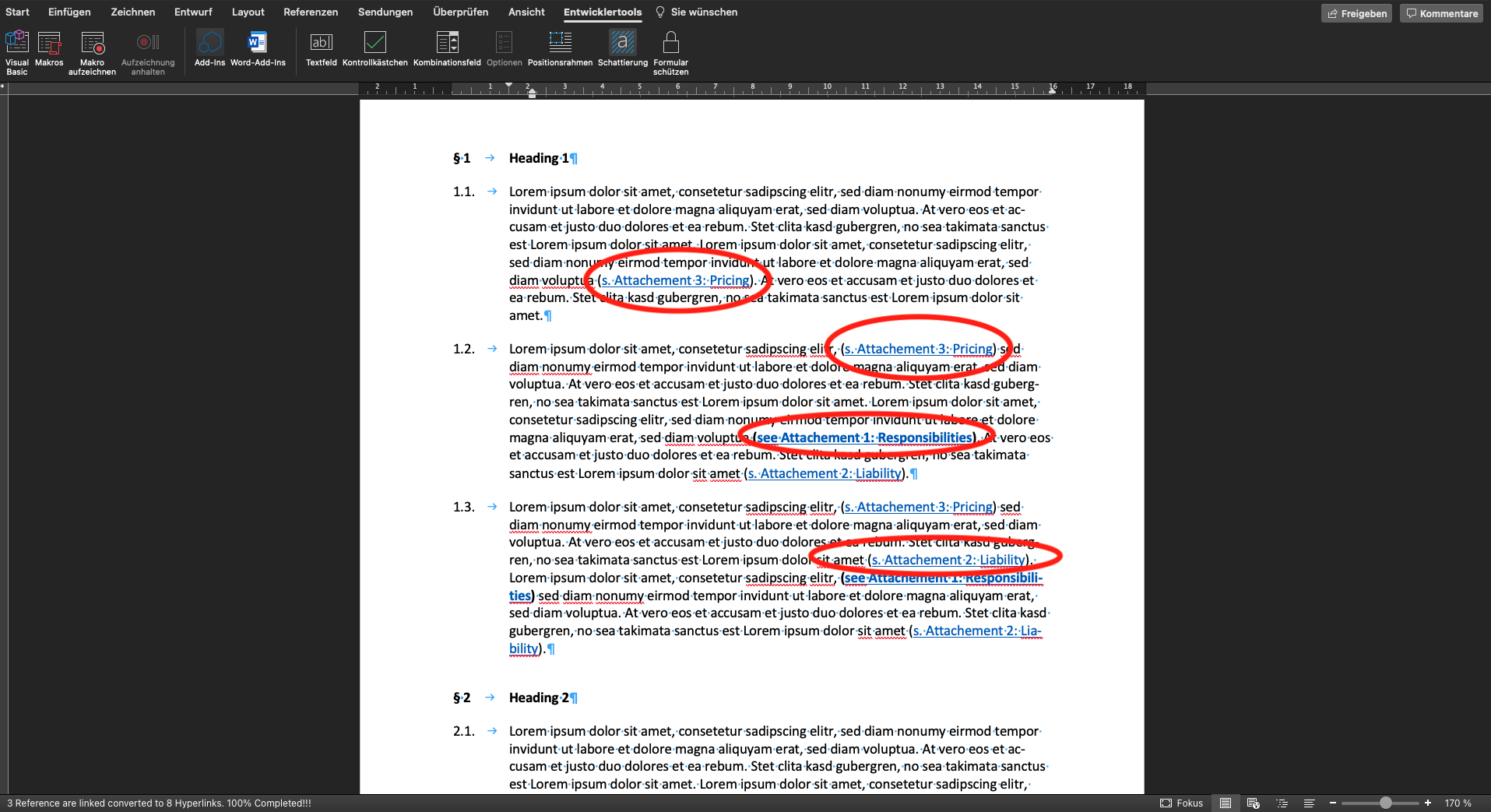
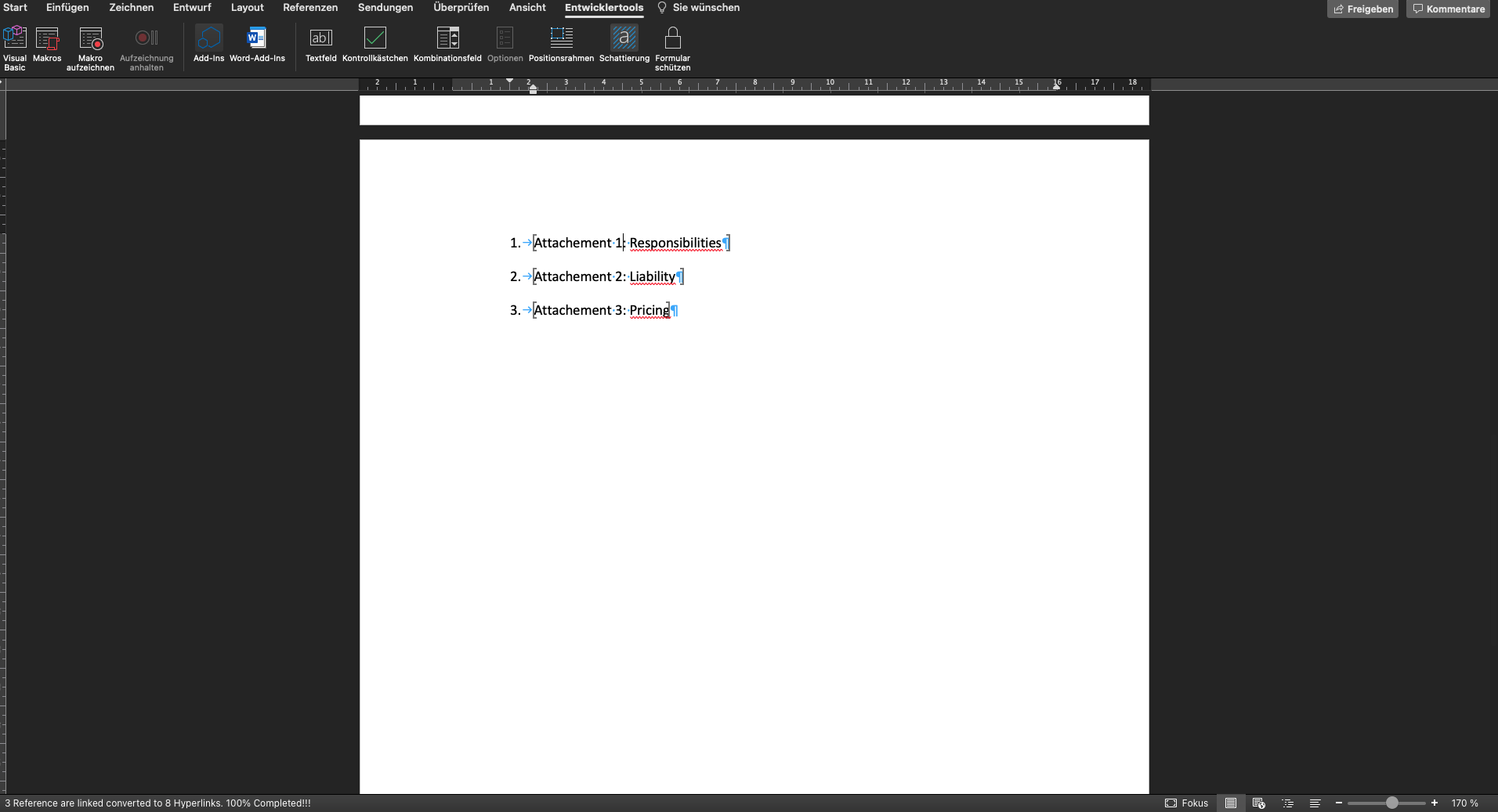
Sub Numbering_N_Bookmarks_Updated_3()
'ADT = Mid(AD.Text, 24, Len(AD.Text))
'Selection.Find.Execute Trim(Left(Mid(AD.Text, 5, Len(AD.Text)), Len(Mid(AD.Text, 5, Len(AD.Text))) - 1)), Forward:=False
Dim BMT, ADT, L1 As String
Dim H As Integer
Dim AD, MyRange As Range: Set MyRange = ActiveDocument.Range
Selection.EndKey wdStory
Selection.Find.Execute "Attachements:", Forward:=False
MyRange.SetRange Start:=Selection.End, End:=MyRange.End
With MyRange.Find
.Text = "{#VN}:"
Do While .Execute
L1 = MyRange.ListFormat.ListString
If Right(L1, 1) = "." Then L1 = Left(L1, Len(L1) - 1)
BMT = MyRange.Paragraphs(1).Range.Text
BMT = Left(BMT, Len(BMT) - 1)
MyRange.Text = L1 & ":"
'=== Bookmark ==='
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Add Range:=MyRange.Paragraphs(1).Range, _
Name:="BByB" & L1
'=================='
Set AD = ActiveDocument.Range
AD.SetRange Start:=AD.Start, End:=MyRange.Start
With AD.Find
.Text = "\(?*\)"
.MatchWildcards = True
.Forward = False
Do While .Execute
AD.MoveEnd wdCharacter, -1
AD.MoveStart wdCharacter, 1
If InStr(.Parent.Text, BMT) Then
AD.Select
Selection.Find.Execute "{#VN}"
Selection.TypeText L1
AD.Select
H = H + 1
'=== Hyperlink ===='
ActiveDocument.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Selection.Range, _
SubAddress:="BByB" & L1
'===================='
Application.StatusBar = L1 & " Reference is in process!!!..."
End If
.Parent.Collapse wdCollapseEnd
Loop
End With
.Parent.Collapse wdCollapseEnd
Loop
End With
Application.StatusBar = L1 & " Reference are linked converted to " & H & " Hyperlinks. 100% Completed!!!"
End SubIMPORTANT: If you want the macro to run automatically when you open the Word file, you can name it "AutoOpen". For help, please contact our support (support@lawlift.com).
